F major triad bass clef – Embark on a musical journey as we delve into the F major triad in bass clef, an essential building block of Western harmony. This comprehensive guide will illuminate the notes, inversions, and uses of this foundational chord, providing a solid foundation for your musical understanding.
From its role in establishing tonality to its pedagogical applications, the F major triad holds a wealth of knowledge that will enrich your musical endeavors. Let’s dive right in!
Key Signature: F Major Triad Bass Clef
The key signature of F major consists of one sharp, which is placed on the F line of the staff. This indicates that all F notes in the piece of music should be played as F sharps.
Placement of Sharps
Sharps are placed on the line or space of the note they affect. In the case of F major, the sharp is placed on the F line, which means that all F notes on the staff are played as F sharps.
Notes in the Triad
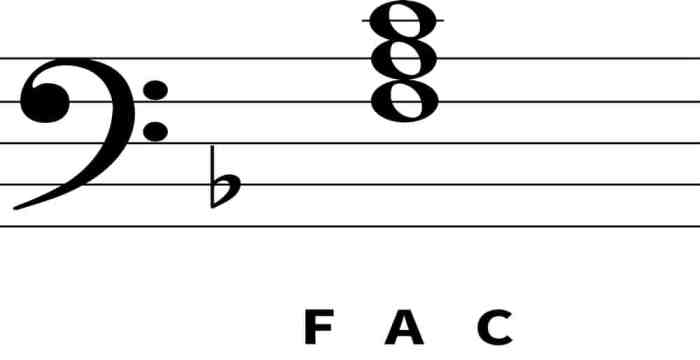
The F major triad consists of three notes: F, A, and C. These notes are arranged in a specific order, with F as the root, A as the third, and C as the fifth. The intervals between these notes are:
F to A
a minor third (3 half steps)
A to C
a major third (4 half steps)These intervals give the F major triad its characteristic sound, which is bright and cheerful.
The F major triad can be played in various inversions. In root position, the root note (F) is in the bass. In first inversion, the third note (A) is in the bass. And in second inversion, the fifth note (C) is in the bass.
While the F major triad in bass clef is a fundamental chord, it’s worth exploring other scales too. Take, for instance, the a minor scale bass clef . Its distinct intervals and somber mood provide a refreshing contrast to the F major triad’s bright and cheerful sound.
Understanding both scales expands your musical vocabulary and enriches your bass clef playing.
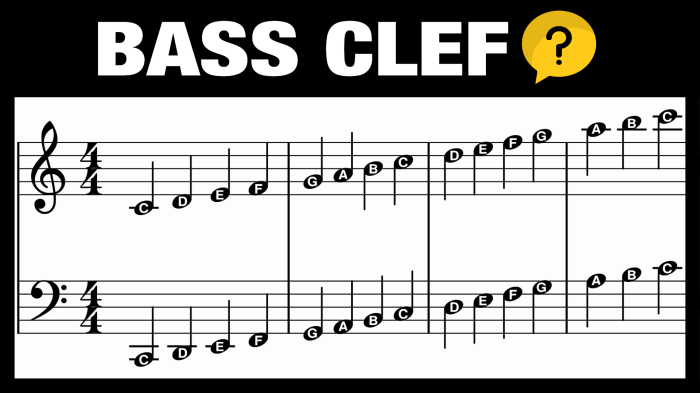
Bass Clef Notation

The bass clef, also known as the F clef, is used to notate the lower-pitched notes in music. It is commonly used for the left hand in piano music and for bass instruments such as the tuba, trombone, and bassoon.
Notation of the F Major Triad in the Bass Clef
The F major triad in the bass clef consists of the notes F, A, and C. The F note is placed on the fourth line of the staff, the A note is placed on the second space, and the C note is placed on the top line.
| F | A | C | |
| Bass Clef |  |
 |
 |
Chord Inversions
Chord inversions are variations of a chord in which the notes are rearranged while maintaining the same harmonic structure. In the case of the F major triad, there are three possible inversions:
First Inversion (F/A)
In the first inversion, the root note (F) is moved up an octave, and the middle note (A) becomes the bass note. The notation for this inversion is F/A, where the slash (/) indicates that the bass note is not the root.
Second Inversion (F/C)
In the second inversion, the root note (F) is moved up two octaves, and the top note (C) becomes the bass note. The notation for this inversion is F/C.
Third Inversion (F/E)
In the third inversion, the root note (F) is moved up three octaves, and the middle note (E) becomes the bass note. The notation for this inversion is F/E.
Uses in Music
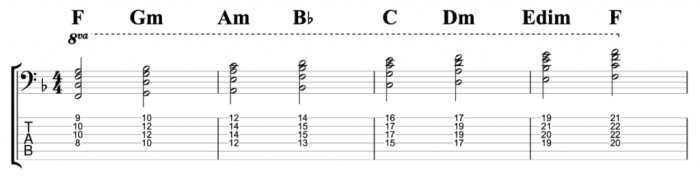
The F major triad is a versatile chord with a bright and uplifting sound. It is commonly used in various musical genres, from classical to contemporary.
Pop and Rock Music
- The F major triad is a common chord in pop and rock music, often used for major key songs or as a transition chord between other chords.
- Examples of songs that feature the F major triad include “Hey Jude” by The Beatles, “Sweet Home Alabama” by Lynyrd Skynyrd, and “Wonderwall” by Oasis.
Jazz and Blues
- In jazz and blues music, the F major triad is used as a dominant chord, meaning it can resolve to a minor chord.
- It is also used as a substitute for the more common dominant seventh chord, creating a more open and relaxed sound.
- Examples of jazz and blues songs that feature the F major triad include “So What” by Miles Davis, “The Thrill Is Gone” by B.B. King, and “Fly Me to the Moon” by Frank Sinatra.
Classical Music
- The F major triad is a fundamental chord in classical music, used in major key compositions.
- It is often used as a tonic chord, providing a sense of stability and resolution.
- Examples of classical pieces that feature the F major triad include “Eine kleine Nachtmusik” by Mozart, “The Four Seasons” by Vivaldi, and “Clair de Lune” by Debussy.
Related Scales
The F major triad is associated with two primary scales: the F major scale and the D minor scale.
These scales share the same notes as the F major triad, but they differ in their starting and ending points.
F Major Scale
The F major scale begins and ends on the note F, and it contains the following notes:
- F
- G
- A
- Bb
- C
- D
- E
D Minor Scale
The D minor scale begins and ends on the note D, and it contains the following notes:
- D
- Eb
- F
- G
- A
- Bb
- C
Historical Significance
The F major triad holds significant historical importance in Western music, particularly in the development of harmony and tonality. During the Baroque period, composers began exploring harmonic progressions beyond simple triads, and the F major triad played a crucial role in this evolution.
Role in Harmonic Progression
The F major triad served as a foundational element in the establishment of major-minor tonality. Its use as a tonic chord in major keys provided a stable harmonic center, while its relationship with other chords, such as the C major triad (subdominant) and the Bb major triad (dominant), formed the basis for harmonic progressions.
Influence on Cadences
The F major triad played a vital role in the development of cadences, which are musical phrases that provide a sense of closure. The perfect cadence, consisting of a progression from a dominant chord to a tonic chord, often employed the F major triad as the tonic in major keys.
Harmonic Function
The F major triad plays a pivotal role in establishing the tonality of the key of F major and creating musical tension and release.
Tonic Function
As the tonic chord, the F major triad serves as the harmonic foundation of the key. It provides a sense of stability and resolution, acting as a “home base” for the music. When other chords are introduced, the F major triad functions as a point of reference, helping to define their harmonic relationship and establish the overall tonal center.
Cadential Function
The F major triad is commonly used in cadences, harmonic progressions that provide a sense of closure or resolution. For instance, the I-V-I cadence (F major – C major – F major) creates a strong sense of finality, emphasizing the tonic key and providing a satisfying conclusion to a musical phrase or section.
Aural Recognition
Recognizing the F major triad by ear requires practice and familiarity with its distinct sound. Here are some tips:
Listen for a clear and strong root note (F) in the bass register. The other notes (A and C) will form a harmonious interval above it.
Audio Example
Here is an audio example of an F major triad:
Practice listening to the F major triad in different contexts and keys to enhance your aural recognition skills.
Pedagogical Applications
The F major triad plays a significant role in music education, serving as a fundamental building block for teaching students about chords, harmony, and music theory.
It introduces students to the concept of triads, which are the most basic type of chord, consisting of three notes.
Importance in Teaching Chords, F major triad bass clef
- Students learn the structure and composition of major triads, which form the foundation of most Western music.
- It helps them understand the relationship between the root, third, and fifth notes of a chord, and how these intervals create a harmonious sound.
Importance in Teaching Harmony
- The F major triad provides a practical example of how chords can be used to create harmonic progressions.
- Students learn how to combine different chords to create musical tension and release, and how to build chord sequences that support melodies.
Importance in Teaching Music Theory
- The F major triad serves as a reference point for understanding key signatures and the relationships between major and minor scales.
- It helps students develop their aural recognition skills and understand the harmonic implications of different chord inversions.
Quick FAQs
What are the notes in the F major triad?
The F major triad consists of the notes F, A, and C.
How many inversions does the F major triad have?
The F major triad has three inversions: first inversion (A in the bass), second inversion (C in the bass), and third inversion (F in the bass).
What is the harmonic function of the F major triad in the key of F major?
The F major triad is the tonic chord in the key of F major, providing a sense of stability and resolution.