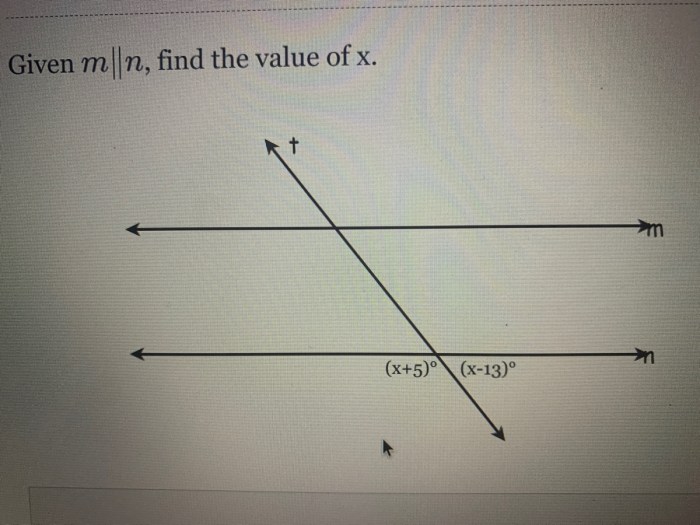
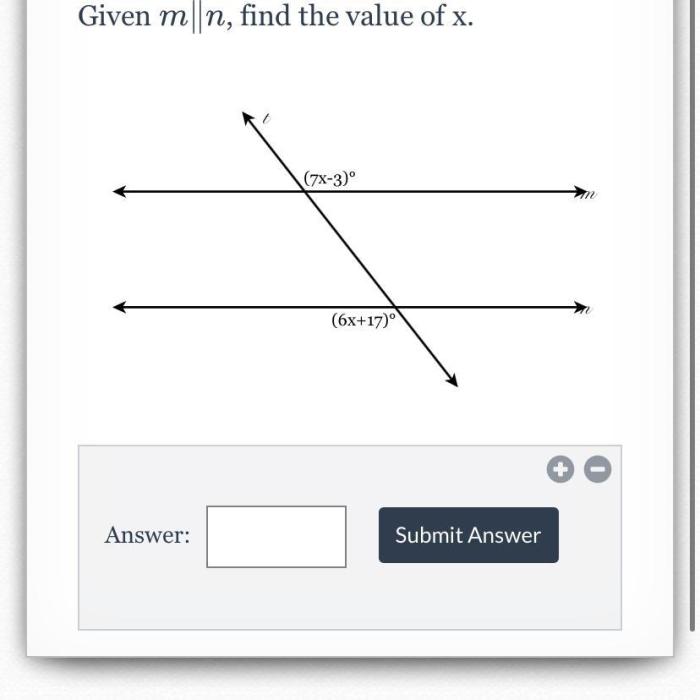
Given m n find the value of x – Embark on a mathematical adventure as we delve into the captivating world of linear equations, where the challenge of finding the elusive value of x awaits. This comprehensive guide will lead you through the intricacies of linear equations, empowering you to solve complex problems with confidence.
Unravel the secrets of variables and constants, explore the fundamental properties of linear equations, and master the art of solving them using substitution and elimination methods. Immerse yourself in real-world applications, witnessing the practical power of linear equations in fields like science, engineering, and economics.
Linear Equations
Linear equations are mathematical equations that represent a straight line on a graph. They are often used to model real-world phenomena, such as the relationship between the distance traveled by a car and the time it takes to travel that distance.
Linear equations have two main components: variables and constants.
Variables, Given m n find the value of x
Variables are letters that represent unknown values. In linear equations, the most common variables are xand y. The value of a variable can change, and the equation will still be true.
Constants
Constants are numbers that do not change. In linear equations, constants are often used to represent known values, such as the slope or y-intercept of a line.
Properties of Linear Equations
- Linear equations can be written in the form y = mx + b, where mis the slope of the line and bis the y-intercept.
- The slope of a line is a measure of how steep the line is. A positive slope indicates that the line is rising from left to right, while a negative slope indicates that the line is falling from left to right.
- The y-intercept of a line is the point where the line crosses the y-axis.
Solving Linear Equations: Given M N Find The Value Of X
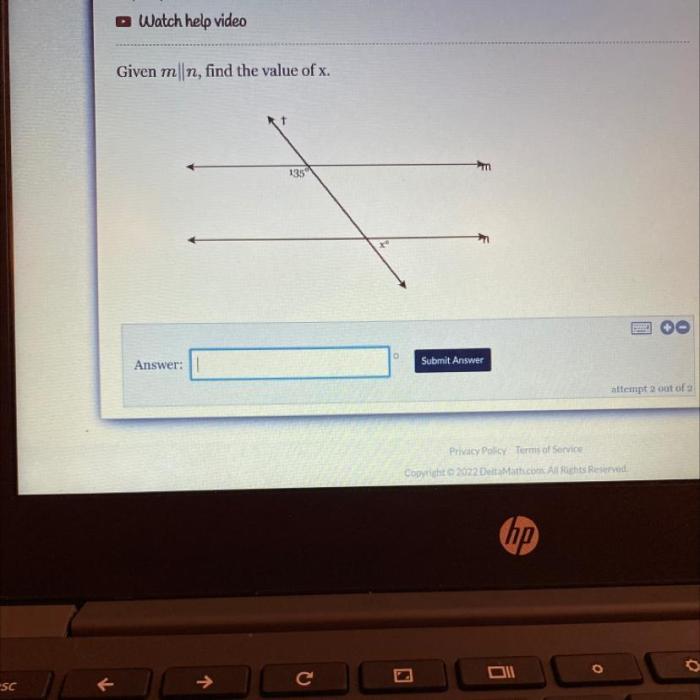
Solving linear equations involves finding the value of a variable that makes the equation true. There are two main methods used to solve linear equations: substitution and elimination.
Substitution method:This method involves substituting the value of one variable into another equation that contains the same variable. The resulting equation can then be solved for the remaining variable.
Elimination method:This method involves adding or subtracting equations to eliminate one of the variables. The resulting equation can then be solved for the remaining variable.
Example
Solve the equation:2x + 3 = 11
Solution:
Let’s say you’re stuck on a math problem like “given m n find the value of x.” Take a break and delve into American history from 1492 to 1877 . It’s a fascinating period that can spark your curiosity. Once you’ve explored the past, return to your math problem with a fresh perspective.
Who knows, you might just crack that tricky equation!
- Subtract 3 from both sides of the equation: 2x = 8
- Divide both sides of the equation by 2: x = 4
Therefore, the solution to the equation is x = 4.
Applications of Linear Equations
Linear equations have a wide range of applications in various fields, including science, engineering, and economics. They provide a powerful tool for modeling and solving real-world problems.
Science
- In physics, linear equations can be used to describe the motion of objects, such as projectiles and falling bodies. For example, the equation $d = vt$ relates the distance traveled ($d$) to the velocity ($v$) and time ($t$).
- In chemistry, linear equations can be used to balance chemical reactions. For example, the equation $2H_2 + O_2 → 2H_2O$ shows the balanced reaction between hydrogen and oxygen to form water.
Engineering
- In civil engineering, linear equations can be used to design structures such as bridges and buildings. For example, the equation $F = ma$ relates the force ($F$) applied to an object to its mass ($m$) and acceleration ($a$).
- In electrical engineering, linear equations can be used to analyze electrical circuits. For example, the equation $V = IR$ relates the voltage ($V$) across a resistor to the current ($I$) flowing through it and the resistance ($R$) of the resistor.
Economics
- In economics, linear equations can be used to model supply and demand. For example, the equation $Q = a + bP$ relates the quantity ($Q$) of a product demanded to its price ($P$) and the constants $a$ and $b$.
- In finance, linear equations can be used to calculate interest and loan payments. For example, the equation $A = P(1 + r)^t$ relates the future value ($A$) of an investment to the present value ($P$), the interest rate ($r$), and the time ($t$).
Systems of Linear Equations
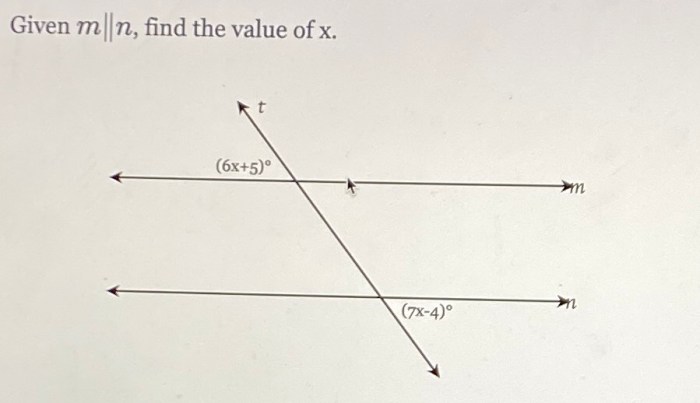
A system of linear equations is a collection of two or more linear equations that involve the same variables. Solving a system of linear equations means finding values for the variables that satisfy all the equations simultaneously.
Methods for Solving Systems of Equations
There are several methods for solving systems of linear equations, including:
- Substitution method:Solve one equation for one variable and substitute the result into the other equation. Solve the resulting equation for the remaining variable.
- Elimination method:Add or subtract multiples of one equation to another equation to eliminate one variable. Solve the resulting equation for the remaining variable.
- Matrix methods:Use matrix operations to transform the system of equations into an equivalent system that is easier to solve.
Examples
Example 1:Solve the following system of equations using the substitution method:
2x + 3y = 7
x – y = 1
Solution:Solve the second equation for x:
x = 1 + y
Substitute this expression for x into the first equation:
2(1 + y) + 3y = 7
Solve for y:
y = 1
Substitute y = 1 back into the expression for x:
x = 1 + 1 = 2
Therefore, the solution to the system of equations is (x, y) = (2, 1).
Example 2:Solve the following system of equations using the elimination method:
3x + 2y = 11
x – 2y = 1
Solution:Add the two equations to eliminate y:
4x = 12
Solve for x:
x = 3
Substitute x = 3 into one of the original equations to solve for y:
3(3) + 2y = 11
y = 1
Therefore, the solution to the system of equations is (x, y) = (3, 1).
Advanced Topics in Linear Equations
Beyond basic linear equations, there are more advanced topics that delve deeper into their applications and complexities. These include parametric equations, inequalities, and absolute value equations, which extend the scope of linear equations and offer insights into more challenging mathematical scenarios.
Parametric Equations
Parametric equations represent a set of equations that describe a curve or line using parameters. Instead of expressing the variables directly, they use one or more parameters that act as independent variables. This allows for greater flexibility in defining and analyzing curves and lines, particularly in contexts involving motion or time.
- For example, the parametric equations x= 2 tand y= 3 t+ 1 define a line with slope 3 that passes through the point (0, 1). The parameter trepresents the position along the line, with different values of tcorresponding to different points on the line.
Inequalities
Inequalities are mathematical statements that express an inequality between two expressions. Unlike equations that represent equality, inequalities use symbols like less than ( <), greater than (>), less than or equal to (≤), and greater than or equal to (≥) to compare the expressions.
- For instance, the inequality 2x+ 5 < 11 represents the set of all values of xthat make the left-hand side expression less than the right-hand side expression. Solving inequalities involves finding the range of values for the variable that satisfy the inequality.
Absolute Value Equations
Absolute value equations involve the absolute value function, which represents the distance of a number from zero on the number line. Absolute value equations are used to solve problems involving distances, magnitudes, and other scenarios where the absolute value is relevant.
- Consider the equation | x– 2| = 5. This equation represents the set of all values of xfor which the distance between xand 2 is equal to 5. Solving absolute value equations requires considering both positive and negative possibilities for the variable.
FAQ Overview
What is the concept of a linear equation?
A linear equation is an algebraic equation of the first degree, meaning it contains only one variable raised to the power of one.
How do I solve a system of linear equations?
There are various methods to solve systems of linear equations, including substitution, elimination, and matrix methods.
What are some real-world applications of linear equations?
Linear equations have wide applications in science, engineering, economics, and many other fields.